Pancreas Anatomy, Functions, and Diseases Medical Library
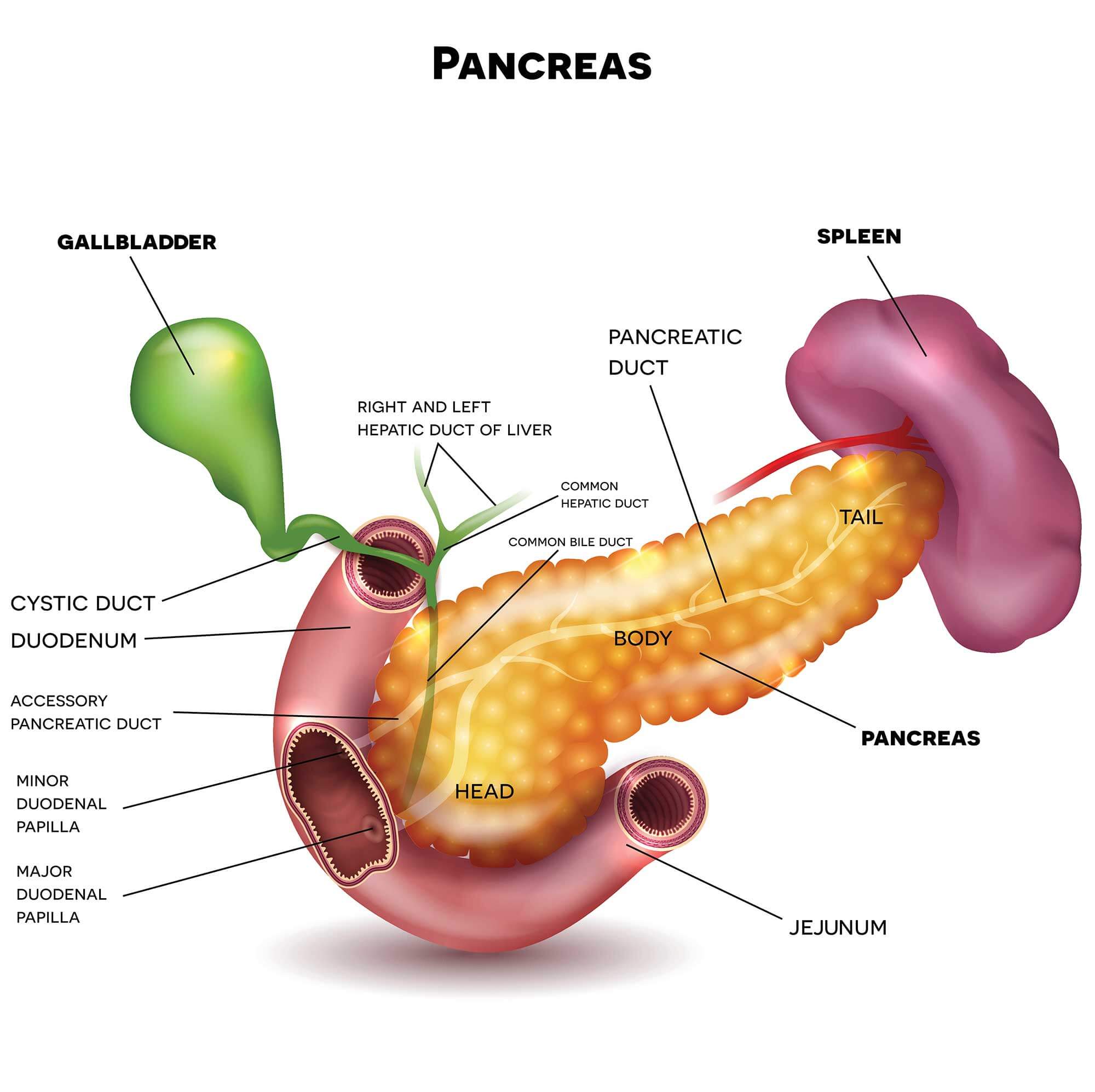
The pancreas is an extended, accessory digestive gland that is found retroperitoneally, crossing the bodies of the L1 and L2 vertebrae on the posterior abdominal wall. The pancreas lies transversely in the upper abdomen between the duodenum on the right and the spleen on the left. It is divided into the head, neck, body, and tail. The head lies on the inferior vena cava and the renal vein and.
Banque de documents pour les SVT du lycée Rôle du pancréas dans la régulation de la glycémie
Le pancréas est un organe vital de l'organisme. Cette glande possède plusieurs fonctions sécrétrices, notamment essentielles à la digestion des aliments et à la régulation de la glycémie.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/pancreas-GettyImages-478188049-5707ce105f9b581408d9a676.jpg)
L'anatomie du pancréas Fmedic
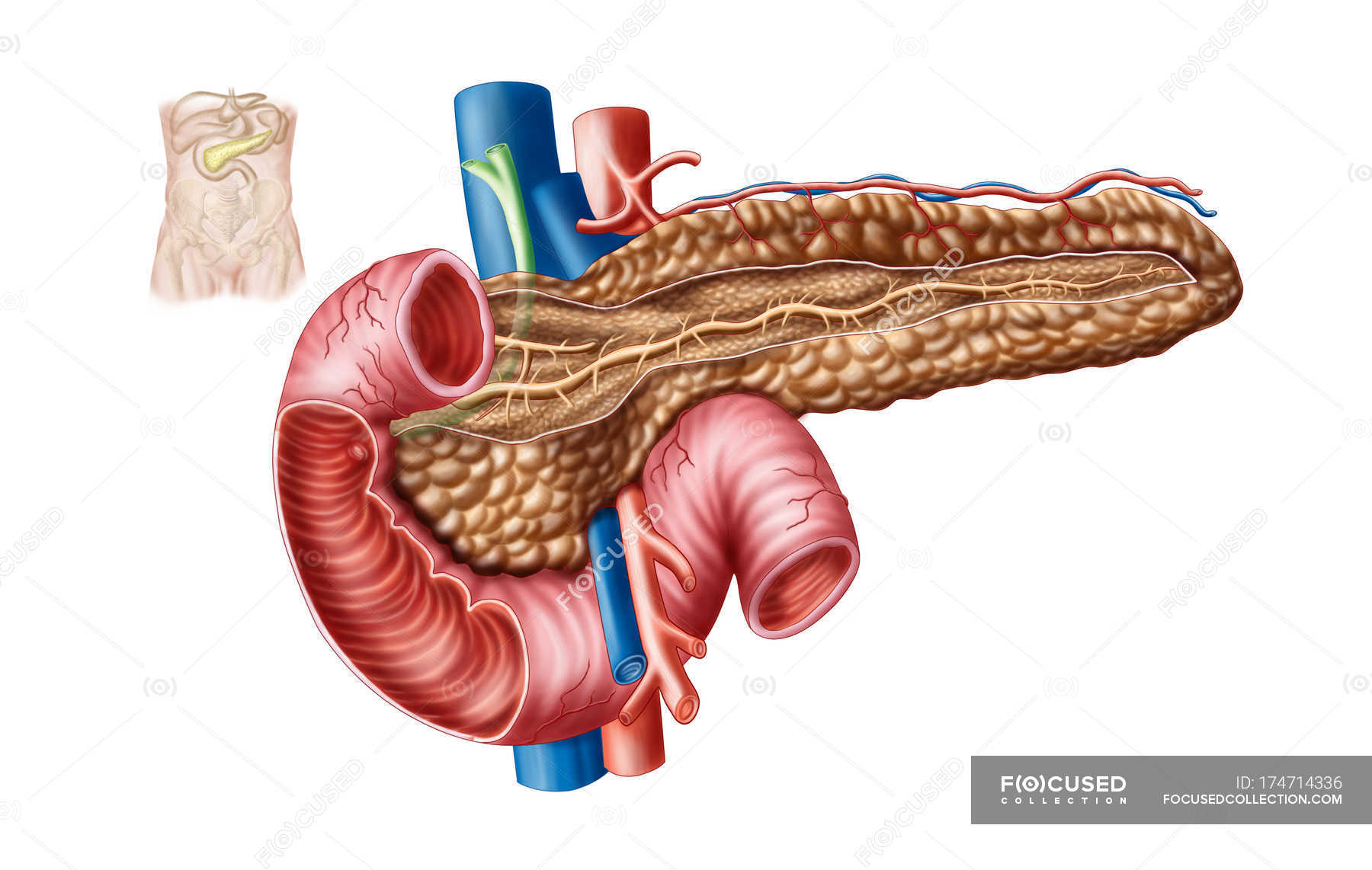
The Body (corpus pancreatis) is somewhat prismatic in shape, and has three surfaces and three borders:The anterior surface (facies anterior) is somewhat concave; and is directed forward and upward: it is covered by the postero-inferior surface of the stomach which rests upon it, the two organs being separated by the omental bursa. Where it joins the neck there is a well-marked prominence, the.

Figure 1 from Making β cells from adult tissues. Semantic Scholar
The pancreas is a retroperitoneal gland that facilitates digestion and metabolism. The pancreatic head and uncinate process adjoin the duodenal curvature; its neck positioned posterior to the pylorus and anterior to the portal venous confluence. The pancreatic body lies posterior to the stomach; the tail enters the peritoneum near the splenic hilum. Unique for a foregut organ, the pancreas.
pancreas Archives Graph Diagram
The pancreas is an oblong-shaped organ positioned at the level of the transpyloric plane (L1). With the exception of the tail of the pancreas, it is a retroperitoneal organ, located deep within the upper abdomen in the epigastrium and left hypochondrium regions. Within the abdomen, the pancreas has direct anatomical relations to several structures.

Pancréas fonction, anatomies et maladies
Anatomy. The pancreas is an elongated gland located deep within the abdomen, tucked in between the stomach and the spine. One end of the pancreas is wider than the other and is called the head: It sits within the curve of the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine) and is divided into two parts: the head proper and the uncinate process.
Medical illustration of pancreas anatomy on white background — view, inferior vena cava Stock
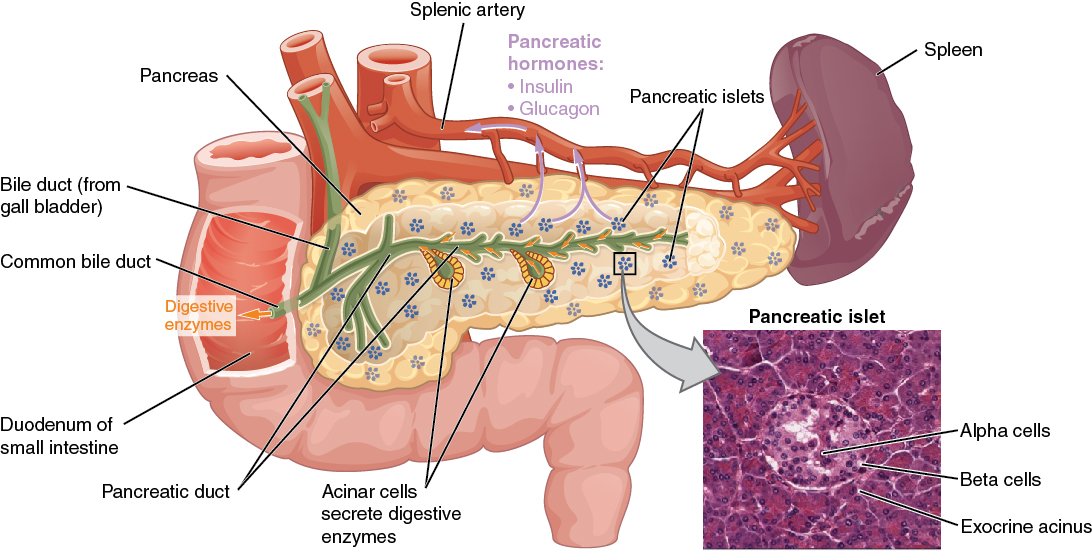
Part 1. The pancreas is an endocrine gland, as it secretes hormones directly into the blood. The endocrine tissues of the pancreas that secrete hormones are called the islets of Langerhans. Within the islets of Langerhans, there are two types of cells: alpha cells and beta cells.

Pancreas and duodenum location Healthcare Illustrations Creative Market
Rapid pulse. Upset stomach. Vomiting. Chronic pancreatitis signs and symptoms include: Pain in the upper belly. Belly pain that feels worse after eating. Losing weight without trying. Oily, smelly stools. Some people with chronic pancreatitis only develop symptoms after they get complications of the disease.

Beating Type 2 Diabetes Give Your Pancreas a Break! Denise A. Pancyrz "Reverse My Diabetes"
The pancreas reveals two different types of parenchymal tissue: exocrine acini ducts and the endocrine islets of Langerhans. The hormones produced in the islets of Langerhans are insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, pancreatic polypeptide, and ghrelin. The pancreatic hormones are secreted by alpha, beta, delta, gamma, and epsilon cells.
Pancreatic Cancer Types Johns Hopkins Medicine
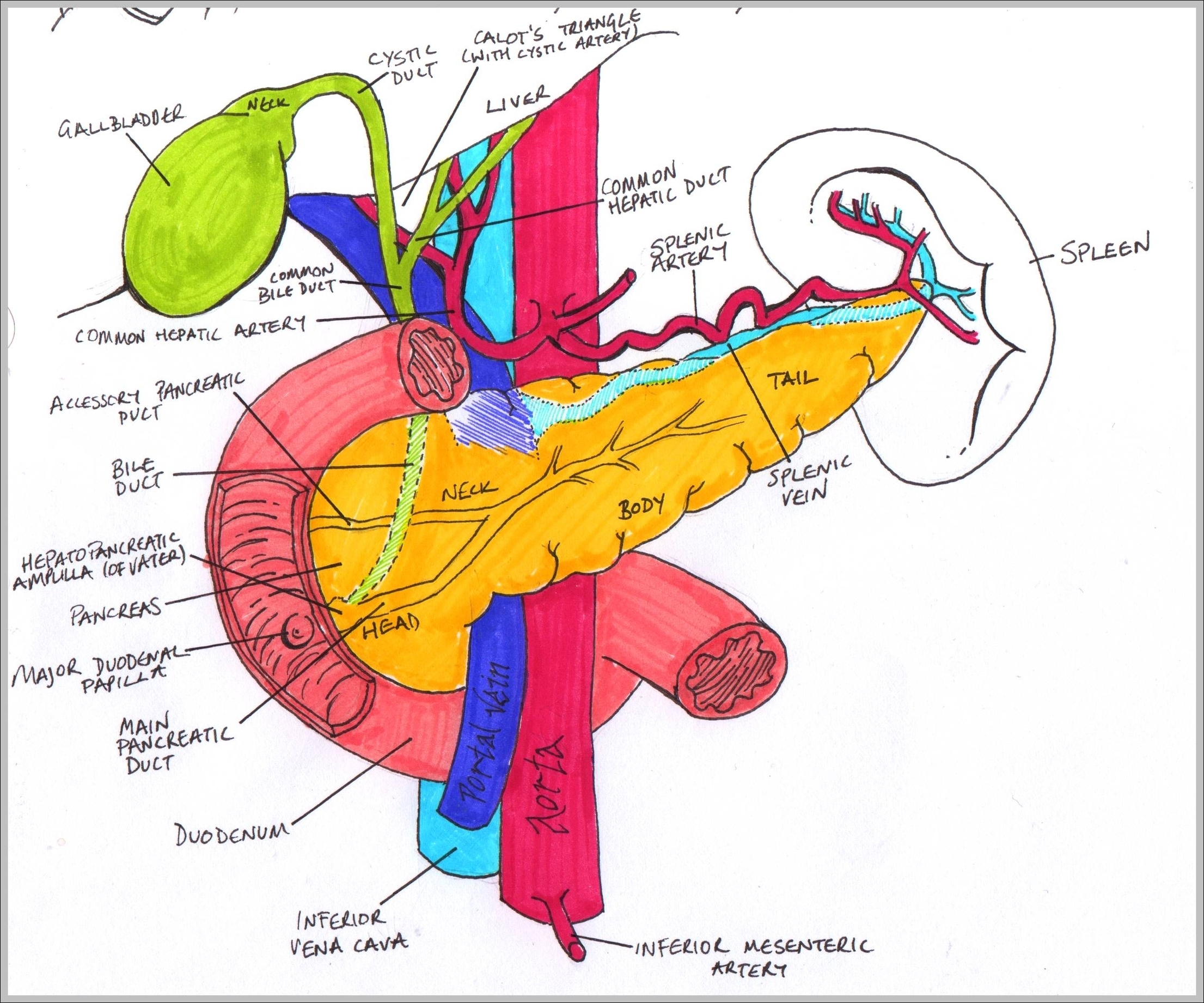
The head is the expanded medial part of the pancreas.It lies directly against the descending and horizontal parts of the C-shaped duodenum which wraps around the pancreatic head. Projecting inferiorly from the head is the uncinate process, which extends posteriorly towards the superior mesenteric artery.Continuing laterally from the head is the neck, a short structure of approximately 2 cm.

Qu'estce qu'un cancer du pancréas ? Fondation ARC pour la recherche sur le cancer
Overview. The pancreas is a large, mixed gland composed of five parts: the head, uncinate process, neck, body and tail. The location of the pancreas is mostly retroperitoneal, except for the tail.This organ extends from the C-shaped curve of the duodenum, passes behind the stomach and finishes at the hilum of the spleen.Several pancreatic ducts extend throughout the pancreas, emptying the.
Pancréas Unité hépatobiliaire et pancréatique de Strasbourg
The pancreas plays a dual role in your bodily functions: Endocrine system. The pancreas secretes hormones, including the blood sugar-regulating hormones: insulin and glucagon. Exocrine system. The.

Pin on Advanced Pathophysiology
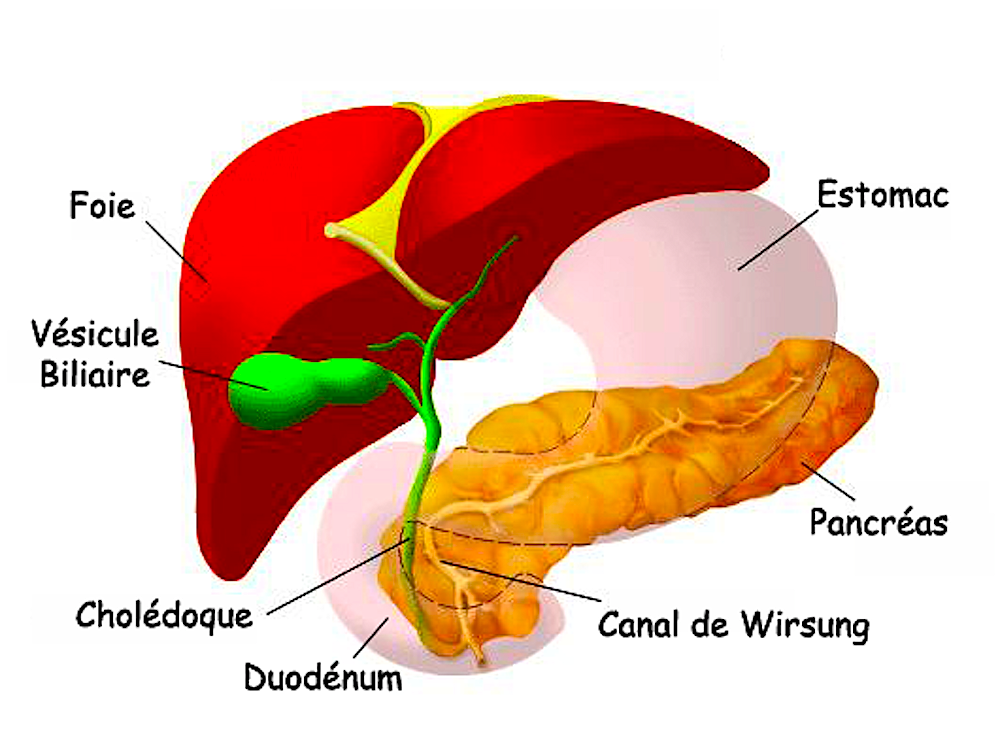
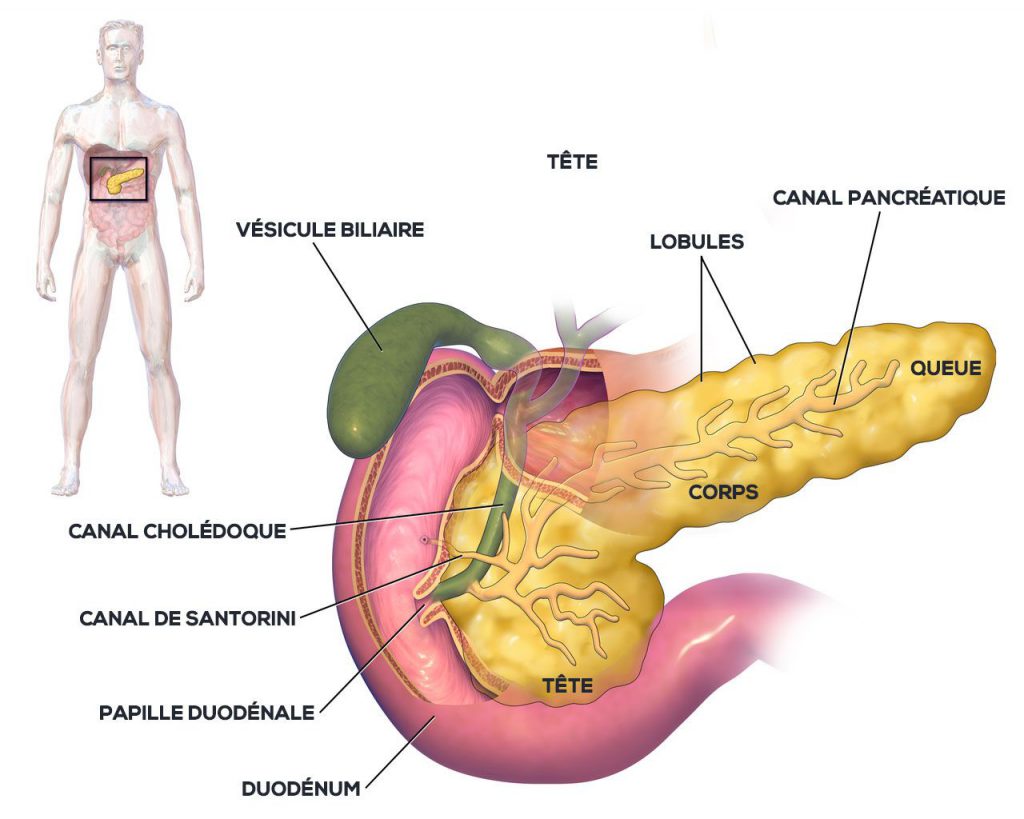
2.1 Anatomie. Le pancréas comprend 4 parties : Tête : contre le duodénum. Col : partie rétrécie qui relie la tête au corps. Corps : partie moyenne qui relie le col à la queue. Queue : extrémité en forme de pointe. Le pancréas a 2 conduits excréteurs : Conduit pancréatique principal de Wirsung : naît au niveau de la queue du.

Pancreas and stomach anatomy anterior view Medical drawings, Medical
The body and neck of the pancreas drain into the splenic vein; the head drains into the superior mesenteric and portal veins. Lymph is drained via the splenic, celiac, and superior mesenteric lymph nodes. Parts of a pancreas: 1: Head of pancreas 2: Uncinate process of pancreas 3: Pancreatic notch 4: Body of the pancreas 5: Anterior surface of.

Anatomie physiologie du pancréas .PDF ETUDEAZ
Anatomie du pancréas. Le pancréas est un organe profondément situé dans la cavité abdominale. Il comporte plusieurs parties qui peuvent être réséquées séparément par le chirurgien qui sont de droite à gauche : la tête dont la partie inférieure et gauche est le crochet ou uncus, l'isthme, le corps et la queue. La tête du.

Pancreas Medical anatomy, Human anatomy and physiology, Anatomy
The pancreas first appears at approximately 5 weeks of gestation as two outpouchings of the endodermal lining of the duodenum just distal to the forming stomach (Figure 5). The outpouchings are the ventral and dorsal pancreas. The dorsal pancreas grows more rapidly than the ventral pancreas. In addition, the ventral pancreas rotates toward the dorsal pancreas as it is "carried" by the.